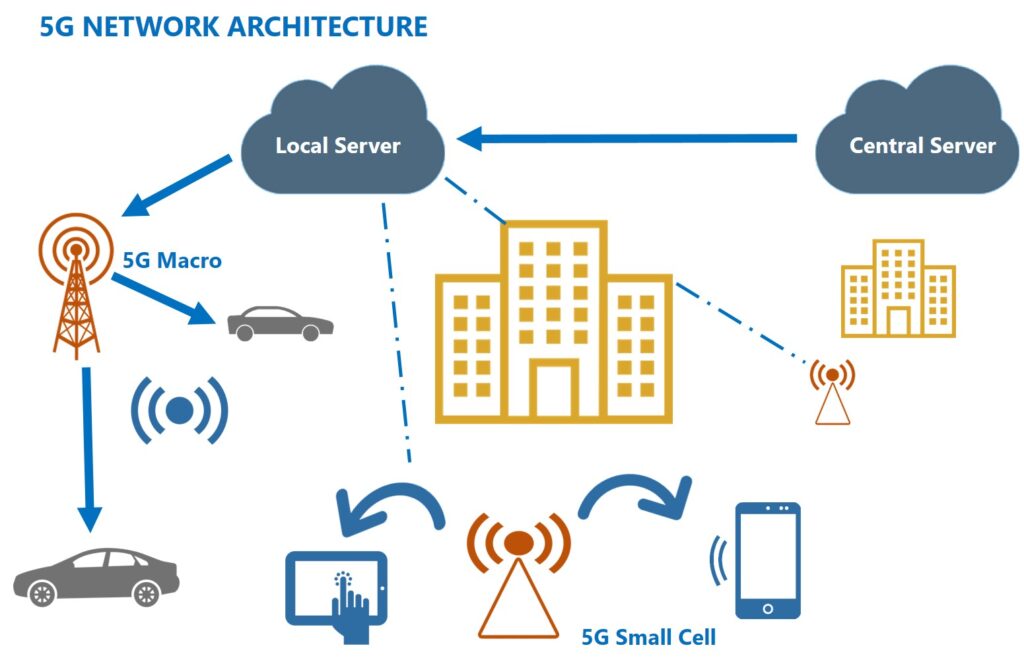
What is 5G?
5G is the next-generation mobile communication technology. Compared to previous generations, it provides higher speeds, lower latency, and greater device capacity. In the IoT space, it is a game-changer for critical applications such as smart cities, autonomous vehicles, industrial robotics, and real-time healthcare solutions.
Why is 5G Used?
- Ultra-low latency: Responses within milliseconds.
- High bandwidth: Perfect for applications requiring large-scale data transfer, such as video and advanced sensors.
- Massive device connectivity: Supports millions of IoT devices simultaneously.
- Seamless mobility: Ensures stable connectivity for moving devices like cars and drones.
Advantages of 5G
- Real-time communication: Essential for autonomous driving and remote surgery.
- Enhanced capacity: Enables thousands of devices to connect within factories or cities simultaneously.
- Network slicing: Dedicated bandwidth and performance for specific applications.
Disadvantages of 5G
- Infrastructure cost: Requires investment in new base stations and hardware.
- Power consumption: May lead to higher energy usage in certain scenarios.
- Coverage limitations: In early stages, consistent nationwide coverage may be difficult to achieve.
Use Cases
- Autonomous vehicles and smart traffic management
- Industrial robots and remote control
- Smart city sensors and video surveillance
- Real-time healthcare and emergency response
Example Scenario
In a smart city, traffic lights are interconnected through 5G. During heavy traffic, real-time data allows the lights to synchronize automatically, reducing congestion and providing priority routes for emergency vehicles.